what is underfloor ventilation
Underfloor ventilation is the process of allowing fresh air to flow beneath the floorboards of a building. This can be achieved through a variety of different methods, including vents, air bricks, and ducts. The aim of underfloor ventilation is to prevent the buildup of moisture and stale air, which can lead to dampness, mold, and rot.
In buildings with suspended timber floors, underfloor ventilation is particularly important. This is because timber floorboards can absorb moisture from the ground, which can lead to rot and decay. By allowing air to flow beneath the floorboards, the moisture is dispersed, reducing the risk of dampness and rot.
Underfloor ventilation can also help to reduce the risk of condensation. In buildings with high humidity levels, such as bathrooms and kitchens, condensation can form on the underside of the floorboards. Over time, this can lead to mold growth, which can be a health hazard. By allowing fresh air to flow beneath the floorboards, the moisture is dispersed, reducing the risk of condensation and mould growth.
types of underfloor ventilation
There are several different types of underfloor ventilation systems available. These include passive ventilation, where vents or air bricks are installed in the walls or foundations of the building, and mechanical ventilation, where fans or ducts are used to circulate air. The type of system used will depend on the specific requirements of the building and the available space.
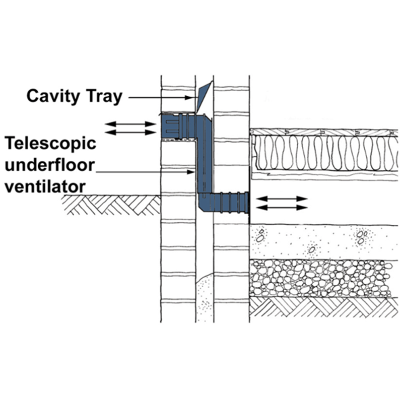
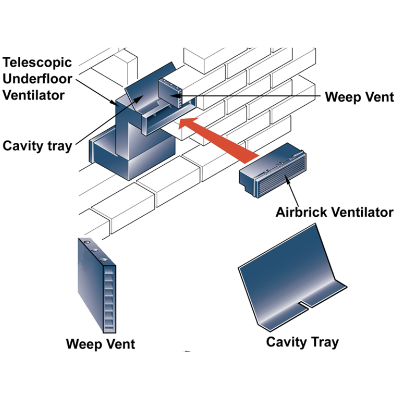
installation
Airbricks for underfloor ventilation should be located on opposite sides of the building. At 3m centres, they will provide 1500mm per metre of the wall which complies with building regulations (see photo).