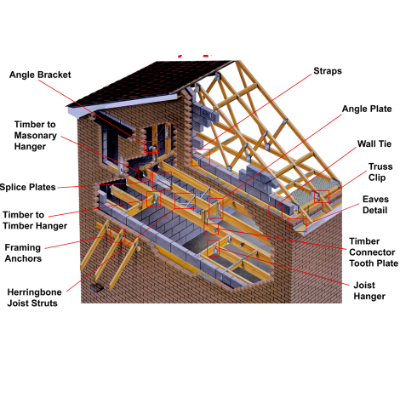
structure of a house
The structure of a house generally refers to the framework or skeleton of the building that provides support for the walls, roof, and floors. It can be broken down into several main components:
1. Foundation: This is the base of the house that rests on the ground and supports the weight of the entire structure. The foundation is typically made of concrete or masonry and is designed to withstand the weight of the house and any external forces, such as wind or earthquakes.
2. Framing: The framing of a house includes the structural components that support the roof and walls. This includes the roof trusses, floor joists, and wall studs, which are typically made of wood or steel.
3. Walls: The walls of a house are the vertical structures that enclose the interior living space and provide support for the roof. Walls can be made of a variety of materials, including wood, brick, stone, concrete, or steel.
4. Roof: The roof of a house covers and protects the interior living space from the elements. It typically includes a framework of roof trusses or rafters, covered with roofing material such as asphalt shingles, metal, or tile.
5. Windows and Doors: These are openings in the walls of the house that allow natural light and air to enter the interior space. They are typically framed with wood or metal and may have glass or other materials to allow visibility and insulation.
Overall, the structure of a house is designed to provide a sturdy and safe living space for its occupants while also protecting them from external forces and the elements.