What are Lead Soakers?
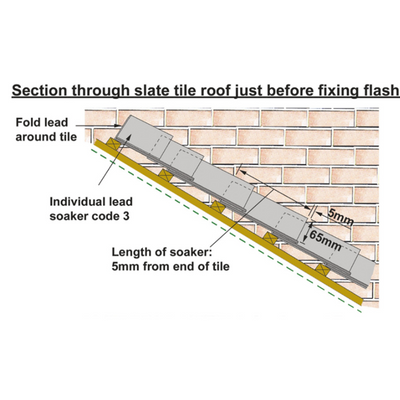
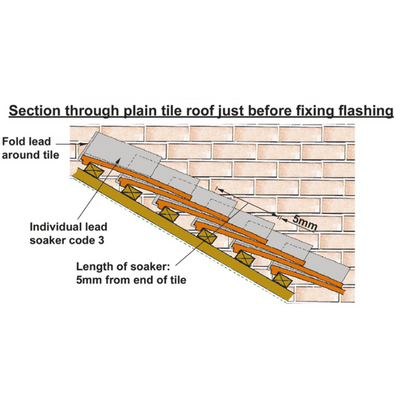
Lead soakers are thin strips of lead used in roofing and construction to create a watertight seal around the base of a chimney or other vertical surface that intersects with the roof. They are typically installed under the roofing material and over the top of the vertical surface, such as a chimney or wall.
The purpose of lead soakers is to prevent water from seeping into the joint between the vertical surface and the roof, which can cause damage to the building's interior and exterior. Without proper flashing, water can seep into the joint and cause rot, mould, and other types of water damage.
Lead soakers are installed by first applying a layer of sealant to the joint between the vertical surface and the roof. The soaker is then installed over the sealant, extending down the roof and up the wall to create a water-resistant barrier. The soaker is typically secured in place using nails or screws and is then sealed with additional sealant to ensure a watertight seal.
Overall, lead soakers are an important component of a building's roofing system, helping to protect the building from water damage and prolong the life of the roof. They are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion and are a popular choice for roofing and construction applications.
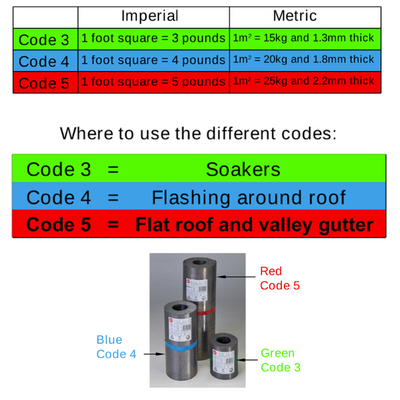
Lead Codes
Lead Codes can be used to determine the weight (and hence the thickness) of the lead sheet. It is vital you are using the correct lead code when building, if done to a good standard, the lead will often outlast the life of that particular building.
Based on pounds weight per foot square, therefore, the higher the code number, the thicker the lead.
In the construction industry, lead codes dictate the proper use and handling of lead-based materials, such as lead flashing, lead pipes, and lead-based paints. For example, the use of lead-based paints in residential applications has been banned in many countries due to the health risks associated with lead exposure.