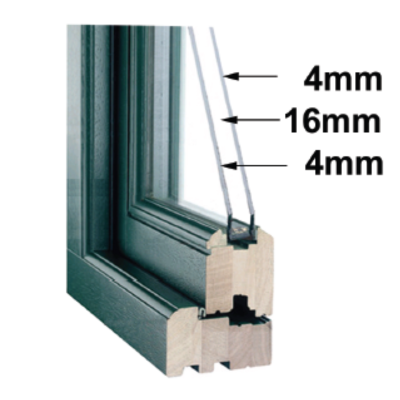
Window Glass
Window glass regulations can vary depending on the location and type of building. Here are some general guidelines:
1. Safety glass: In many countries, safety glass is required for certain types of windows, such as those in doors, near stairs, or in bathrooms. Safety glass is designed to minimize the risk of injury if it breaks, and it is often required by building codes.
2. Fire safety: In some locations, building codes require that windows meet certain fire safety standards. This may include requirements for the size and type of window, as well as the materials used for the frame and glass.
3. Energy efficiency: Many countries have regulations or standards for the energy efficiency of windows. These standards may specify the type of glass or glazing that must be used, as well as requirements for insulation and air leakage.
4. Building codes: Building codes in general will have specific requirements for windows in buildings. These may include requirements for the minimum size of windows, the placement of windows, and the type of glass that can be used.
5. Historical preservation: In some locations, regulations may be in place to protect historic buildings or neighbourhoods. These regulations may include restrictions on the types of windows that can be used, as well as requirements for the appearance of the windows.
It's important to check with your local building authority or regulatory body to determine the specific requirements that apply to your situation.

Door Glass
Door glass regulations can also vary depending on the location and type of building. Here are some general guidelines:
1. Safety glass: As with windows, safety glass may be required for certain types of doors, such as those with large glass panels or those near stairs. This is to minimize the risk of injury if the glass breaks.
2. Glazing size and placement: Building codes may specify the maximum size of glazing that is allowed in doors, as well as the placement of glazing within the door. This is to ensure that the door is structurally sound and secure.
3. Fire safety: Some building codes require that doors meet certain fire safety standards. This may include requirements for the size and type of glazing, as well as the materials used for the frame and glass.
4. Accessibility: Regulations may require that certain types of doors, such as those in public buildings, be accessible to people with disabilities. This may include requirements for the size and placement of glazing, as well as the type of glass used.
5. Building codes: As with windows, building codes will have specific requirements for doors in buildings. These may include requirements for the minimum size of doors, the placement of doors, and the type of glazing that can be used.
Again, it's important to check with your local building authority or regulatory body to determine the specific requirements that apply to your situation.
Trickle vent
A trickle vent is a small opening in a window or door that allows a controlled amount of ventilation to occur even when the window or door is closed. The purpose of a trickle vent is to improve indoor air quality by allowing fresh air to circulate while also preventing condensation and reducing the risk of mold growth.
Trickle vents can be particularly useful in homes and buildings that are well-insulated or have low levels of natural ventilation. Without proper ventilation, indoor air can become stale and humid, which can lead to a range of health problems, including allergies and respiratory issues.
Trickle vents also help to regulate the temperature and humidity levels inside a building, which can improve overall comfort and reduce the need for artificial heating or cooling. Additionally, they can help to reduce the build-up of pollutants and odors inside a building, which can be particularly important in homes or buildings located near busy roads or industrial areas.